Essential brain food: Here’s why you probably need DHA supplements
01/22/2018 / By Michelle Simmons

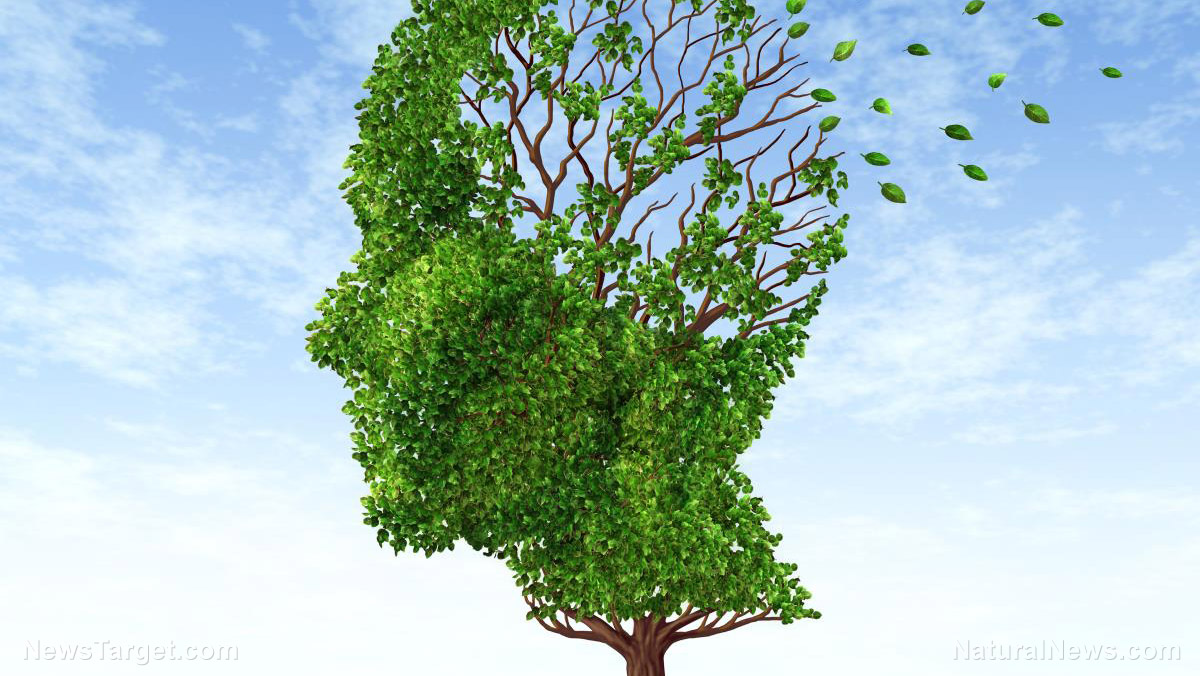
More than half, or 60 percent, of the brain is composed of fat. Thus, healthy fats play a crucial role in the brain’s development. In particular, omega-3 fatty acids are the most important when it comes to the brain’s structure and performance. These are essential fats that can be found in foods such as fish, vegetable oils, nuts, flaxseeds, flaxseed oil, and leafy vegetables, and supplements. There are three main omega-3s — eicosapentaenoic acid (EPA), docosahexaenoic acid (DHA), and alpha-linolenic acid (ALA). These omega-3s are the preferred building blocks of brain and nerve cells. Without these, the brain will utilize whatever fats are available, which results to poor brain cells. Among the three, DHA appears to be the most essential omega-3 for the brain.
DHA and its benefits in all stages of life
DHA makes up 97 percent of the omega-3 fatty acids in the brain. It is a primary structural component of the brain part that is responsible for memory, language, creativity, emotion, and attention. In addition, DHA is involved in brain cell communication. It supports the best levels of numerous essential neurotransmitters, such as dopamine, serotonin, GABA, and acetylcholine. Moreover, it increases the amount of neurotransmitters which allow the brain to utilize these brain chemicals better. There are even fossil evidence that indicate that the brain depends on seafood for DHA.
DHA plays a crucial role on the brain’s health in all stages of life. In fact, it is important for the brain development of newborns. Mothers are suggested to take DHA supplements for the brain development of their baby. Babies get their DHA from breast milk or baby formulas supplemented with DHA. In children with depressive disorder, studies show that DHA supplementation reduced their depressive symptoms, while it improved the attention, hyperactivity, defiant behavior, and sleep of those with attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). For adults, DHA helps preserve brain volume by slowing down brain aging as the brain naturally shrinks with age. It also increases brain plasticity, improves mood and enhances mental health. Furthermore, it increases the number of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF), the protein that maintains healthy brain cells and prompts new brain cell formation.
In older adults with mild cognitive problems, a study found that DHA supplementation may enhance their memory and learning. It helps them keep mentally fit and reduce the risk of age-related mental diseases like neuroinflammation, macular degeneration, and Parkinson’s disease.
Where to get DHA?
DHA is not produced in the body, therefore it must be acquired from foods or supplements. High amounts of DHA can be taken from cold-water fish, fatty fish, such as salmon, tuna, sardines, shellfish, and herring. Pregnant women or those who plan to become pregnant must not eat specific types of fish, including king mackerel, shark, swordfish, and tilefish. The fatty acid can also be found in nuts, flax seeds, and sea vegetables, but only in low amounts. As a supplement, DHA is available in two common forms — fish oil capsules and DHA from algae. Fish oil capsules contain both DHA and EPA, while the latter only has DHA. Although there is no Recommended Dietary Allowance (RDA) for DHA, experts suggest to take 500 to 1,000 milligrams (mg) of total omega-3s a day to remain healthy and fight deficiency.
Read more stories on brain health at Brain.news.
Sources include:
Tagged Under: Brain, cognitive function, DHA, DHA supplements, fatty acids, nutrients, omega 3, supplements
RECENT NEWS & ARTICLES
COPYRIGHT © 2017 ALZHEIMERS NEWS